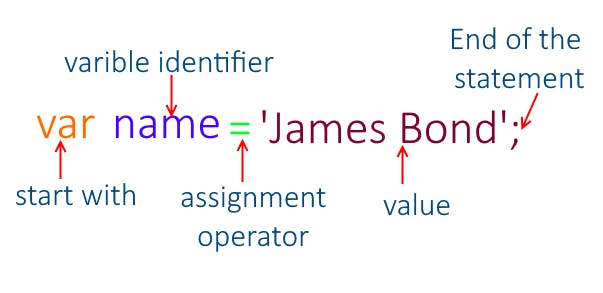
Variable Identifiers
All JavaScript variable must be identified by unique name, this name call identifiers. Identifiers can be short name like ( x, y, …) or more descriptive name like (age, sum, …).
Rule of constructing name
- Name can contain letter, digits, underscores and dollar sign
- Names must begin with letter
- Names can be begin with $ and _
- Names are case sensitive (y and Y are different variables)
- Reserved words (JavaScript keyword) can’t be used as name
JavaScript can holed many type of data like string, number
var pi = 3.4;
var person = "Ahmed"
Declaring variable
Creating variable in JavaScript call declaring variable
var CarName;
To assign a value to the variable use ( = )
carName = "Volvo"
Undefined
Variable declared without value
var carName;
//undefined
Let
The Let keyword was introduced in ES6(2015) Variables defined with let must be declared before use Variables defined with let cannot be redeclared That min we can’t do this
let x = "John Doe";
let x = 0;
Block scope
Before ES6(2015), JavaScript had only global scope and function scope in ES6(2015) introduced two important new JavaScript keyword: Let and Const this tow keyword provide block scope in JavaScript so the variables declare inside {} can’t be accessed from outside the block
{ let x = 2;}
// x can NOT be used here
Variables declared with the var can't have Redeclaring variables using var can impose problem
var x = 10;
// Here x is 10
{
var x = 2;
// Here x is 2
}
// Here x is 2
Redeclaring
With keyword var is allowed anywhere in program With let you can’t redeclaring variable in same scope
var x = 2;
// Allowed
let x = 3;
// Not allowed
{
let x = 2;
// Allowed
let x = 3
// Not allowed
}
{
let x = 2;
// Allowed
var x = 3
// Not allowed
}
Let hoisting
Variable defined with var can be hoisted to the top and can be initialized at any time meaning you can use variable before it is declared Variable defined with let are also hoisted to the top but not initialized meaning you can’t use variable before it is declared (you must declare variable before used)
Const
The Const keyword was introduced in ES6(2015) Variables defined with Const cannot be redeclared Variables defined with Const can’t be Reassigned Variables defined with Const have block scope
Can’t be Reassigned
const PI = 3.141592653589793;
PI = 3.14;
// This will give an error
PI = PI + 10;
// This will also give an error
You can’t reassigned PI variable because it is const
Must be assigned
const PI = 3.14159265359;
You can’t do this
const PI;
PI = 3.14159265359;
When to use const variable
Always use const variable when you declare
- Array
- Object
- Function
- RegExp
Constant object and array
The const keyword it dose not define constant value. It defines constant reference to the value Because of that you can’t
- Reassign a constant value
- Reassign a constant array
- Reassign a constant object
But you can
- Change a constant array
- Change a constant object
Constant array
You can do
// You can create a constant array:
const cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];
// You can change an element:
cars[0] = "Toyota";
// You can add an element:
cars.push("Audi");
You can’t do
const cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];
cars = ["Toyota", "Volvo", "Audi"]; // ERROR